The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope. (Atomic mass is also referred to as atomic weight, but the term 'mass' is more accurate.)
- Element number 5 is boron (B). That means every atom of boron has 5 protons. The most common isotope (about 80% of naturally occurring boron) of boron has 6 neutrons too, for a total of 11 nucleons (protons + neutrons). Its mass number is 11.
- Element Boron (B), Group 13, Atomic Number 5, p-block, Mass 10.81. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.
- Boron-10 atom is a stable isotope of boron with relative atomic mass, 19.9 atom percent natural abundance and nuclear spin 3+.
- Isotopes of Boron (click to see decay chain): 6 B 7 B 8 B 9 B 10 B 11 B 12 B 13 B 14 B 15 B 16 B 17 B 18 B 19 B 11 B.
For instance, it can be determined experimentally that neon consists of three isotopes: neon-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons in its nucleus) with a mass of 19.992 amu and an abundance of 90.48%, neon-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons) with a mass of 20.994 amu and an abundance of 0.27%, and neon-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons) with a mass of 21.991 amu and an abundance of 9.25%. The average atomic mass of neon is thus:
| 0.9048 | × | 19.992 amu | = | 18.09 amu |
| 0.0027 | × | 20.994 amu | = | 0.057 amu |
| 0.0925 | × | 21.991 amu | = | 2.03 amu |
| 20.18 amu |
The atomic mass is useful in chemistry when it is paired with the mole concept: the atomic mass of an element, measured in amu, is the same as the mass in grams of one mole of an element. Thus, since the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams. The same concept can be extended to ionic compounds and molecules. One formula unit of sodium chloride (NaCl) would weigh 58.44 amu (22.98977 amu for Na + 35.453 amu for Cl), so a mole of sodium chloride would weigh 58.44 grams. One molecule of water (H2O) would weigh 18.02 amu (2×1.00797 amu for H + 15.9994 amu for O), and a mole of water molecules would weigh 18.02 grams.
The original periodic table of the elements published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869 arranged the elements that were known at the time in order of increasing atomic weight, since this was prior to the discovery of the nucleus and the interior structure of the atom. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number instead.
What is the mass number of boron?
Boron (5 B) naturally occurs as isotopes 10 B and 11 B, the latter of which makes up about 80% of natural boron. There are 13 radioisotopes that have been discovered, with mass numbers from 7 to 21, all with short half-lives, the longest being that of 8 B, with a half-life of only 770 milliseconds (ms) and 12 B with a half-life of 20.2 ms.
2 Answers
Mass Number Of Boron With 4 Neutrons
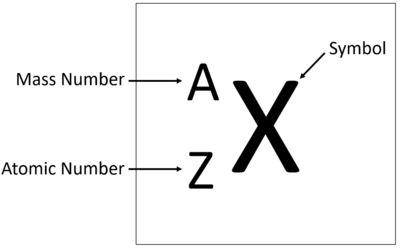
Explanation:
To a first approx.
Do you agree?
The mass number of the most common isotope of boron is 11.
Please see the more detailed explanation below.
Explanation:


This is a slightly tricky question, because a mass number is for a particular isotope of an element, not the element itself.
Element number 5 is boron (B). That means every atom of boron has 5 protons.
The most common isotope (about 80% of naturally occurring boron) of boron has 6 neutrons too, for a total of 11 nucleons (protons + neutrons). Its mass number is 11.

Some naturally occurring boron (about 20%) has 5 neutrons, for a total of 10 nucleons, and a mass number of 10.
Mass Number Of Boron 11
It is also possible to make isotopes with more than 6 or less than 5 neutrons.
The mass number of the most common isotope of boron is 11.
Boron Whose Mass Number Is 10
Related questions
